German Aircraft Carrier - Here's what you need to remember: And of course there is the question of who controls a European ship. Where will it be built, who will build it and what aircraft will it fly (France builds its own Rafale M jets, but Britain opts for the F-35)? What authority does he command and submit to dangerous situations?
Annegret Kramp-Karrenbauer, the president of Germany's Christian Democratic Union and a possible successor to Chancellor Angela Merkel, caused a stir when she suggested that European countries work together to build an airplane.
German Aircraft Carrier

"Germany and France are already working together on the project of a future European fighter jet," he wrote in an article in the German newspaper Die Welt (English translation here). "The next step can be the beginning of the symbolic work to create a common European plane to show the role of Europe to the whole world as a force that ensures security and peace."
German Imperial Navy Aircraft Carrier
Merkel apparently supported the idea. "It's right and good that we have tools like this on the European side, and I'm happy to work on it."
Surprisingly, Kramp-Karrenbauer actually rejected a call by French President Emmanuel Macron for more European integration. "There is no definition of a high level of Europe that can achieve the goal of a Europe made of representatives of the government and able to work," he wrote.
But there is still room for a common European policy, including the European Security Council including Britain. And, a European airliner.
Interestingly, even Kramp-Karrenbauer called the Euro bearer a "symbolic movement." The importance of an airfield is that it is a mobile airfield that can place aircraft near areas that may be difficult to reach for conventional aircraft. This is very important for some countries that have global interests or examples, such as the United States, Russia, China and even the United Kingdom and France, two European countries that operate ship. For example, Britain has sent its new aircraft, HMS
Here's Why The Germans Never Used Their Only Aircraft Carrier In Combat During Wwii
, and the new aircraft proposed to replace it, indicate that France's colonial interests remain in places like the Indian Ocean.
But most European countries don't usually send ships to offshore areas, or they have small ships, or they are locked and don't need ships. An aircraft carrier would be of limited value in a conflict with Eastern Russia or Northern Europe, or the Baltic States. Special defenses and a barrier of guided ships will be needed to survive in the Baltic Sea against Russian naval and air defenses, as well as anti-ship missiles such as the hypersonic K-300P Bastion. Even the US Navy, with all its money and resources, is concerned about the survival of its supercarriers. It is hard to imagine that Europe will design and finance a more powerful and sustainable ship than the US $ 13 billion
Europe has interests in the Mediterranean. In 2018, Britain and France joined the United States in launching air and missile strikes against the Syrian government. But ground flights can operate from Cyprus or Italy. The European Union also wants to stop the large number of illegal immigrants sailing across the Mediterranean to Europe. A boat would cost the Coast Guard dearly.
Perhaps the real question is not what a ship will bring, but what Europe will deliver. The German military was ineffective, with Typhoon planes that didn't fly, ships that couldn't sail and an ineffective army that was a fraction of its Cold War strength. Many NATO members do not spend even the 2 percent of their GDP that they are supposed to give to defense, leaving little money for an expensive fleet, aircraft carriers and missile boats. Many of the threats facing European countries, from Russian invasions to cyber warfare, cannot be solved by a ship.
German Cvn Adenauer Class By Silver 70chev On Deviantart
And of course there is the question of who controls a European ship. Where will it be built, who will build it and what aircraft will it fly (France builds its own Rafale M jets, but Britain opts for the F-35)? What authority does he command and submit to dangerous situations?
Unless Continental Europe plans to attack Britain in a new Operation Sealion, it's a fleet of the wrong choice. The German navy—the Kaiserliche Marine, the Reichsmarine, and the Kriegsmarine—all planned to build aircraft, although none would see service. These ships were based on the knowledge gained during the experiments with aircraft operated by the Kaiserliche Marine during the First World War. Among these was the light aircraft SMS Stuttgart, which was converted to carry three aircraft,
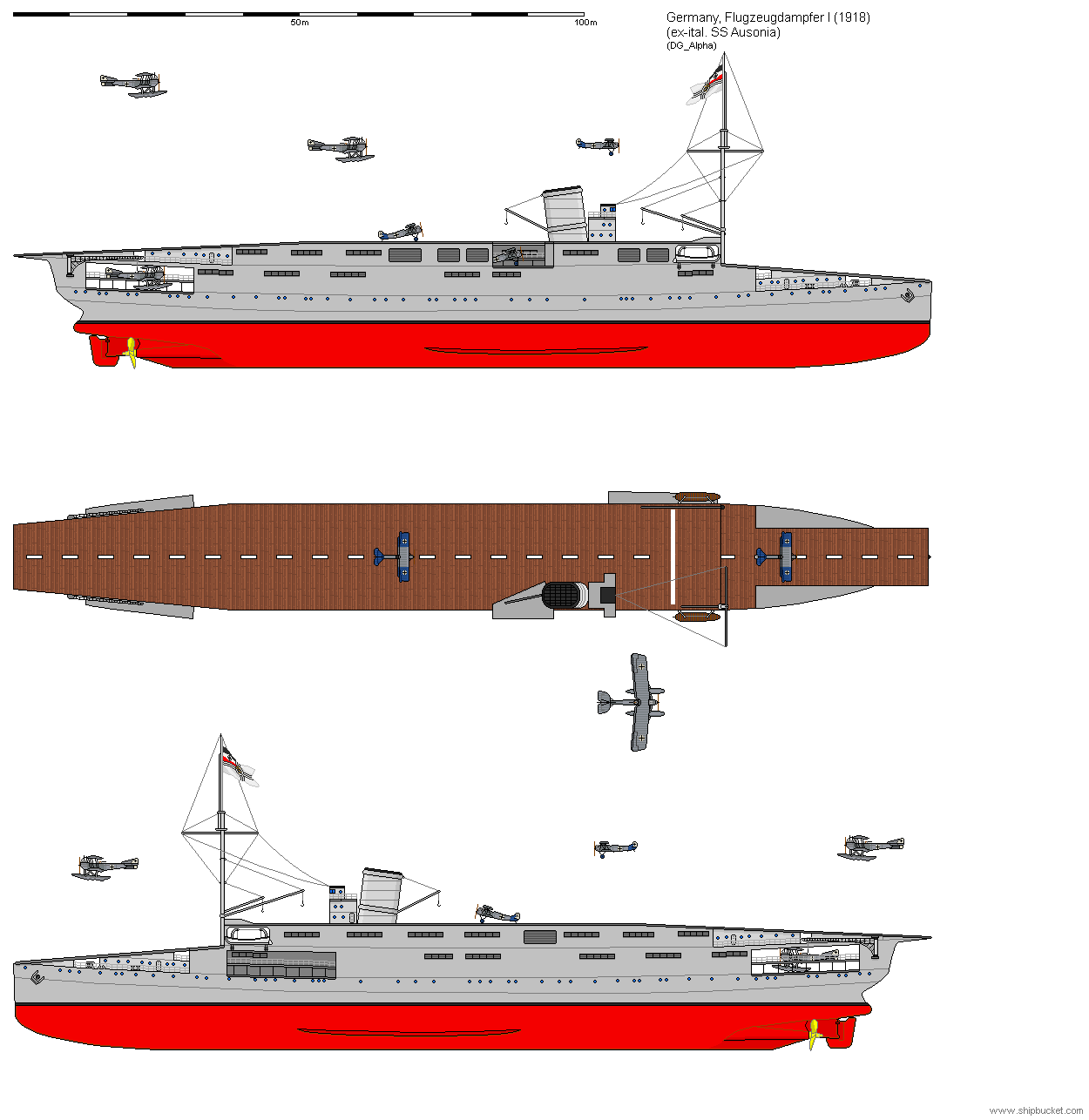
However, these ships did not meet the needs of high-speed ships, so a more ambitious plan was put in place to convert the unfinished passenger car SS Ausonia into an aircraft carrier planned at the beginning of 1918. The work could not be completed before the war in November, however, because resources could not be diverted from the U-base. boat
From the mid-1930s, the Reichsmarine began research projects for a new type of aircraft carrier to meet the needs of the modernization of the German Navy; By 1936 these ideas had arrived in the class of the Graf Zeppelin, the first member of which was laid down in December of that year for the planned Kriegsmarine. A second carrier, designated Flugzeugträger B, followed in 1938, and Plan Z of fleet expansion called for another carrier. two were of a new design to be used in 1945. However, no ships of the Graf Zeppelin class would be completed. until the start of World War II in September 1939; ceased operations in early 1940, and the Flugzeugträger B was discontinued. Work on the Graf Zeppelin resumed in 1942, but was halted again in early 1943 due to high demand. During this second construction period, the Kriegsmarine proposed converting several passenger ships and two unfinished cruisers into auxiliary aircraft carriers, although none of these were completed. , and by 1945 all had been destroyed or looted by the Allied forces.
German Aircraft Carrier “graf Zeppelin” Pictures
The first planned aircraft was established in 1918, at the end of the First World War; the German Kaiserliche Marine (Imperial Navy) first experimented with aircraft operated from ships such as the battleship Friedrich Carl.
A major step forward came in 1918, when the Stuttgart light aircraft was converted into a dedicated commercial aircraft. That same year, the Navy decided to convert the Ausonia passenger ship, which was under construction, into an aircraft carrier.
However, the construction priorities of the last year of the war meant that the ship would not be finished. The available land was used to build U-boats for merchant raids.

With no conversion work done, the plan was abandoned. The unfinished Ausonia was demolished for 1922.
Re5164 German Aircraft Carrier Graf Zeppelin
The Kriegsmarine began design work on a new class of aircraft carriers in the mid-1930s; the first proposal for a 22,000-longton (22,000 t) ship with 50 aircraft, was prepared in 1935.
The Anglo-German Naval Agreement, signed that year, allowed Germany to build up 35 percent of the strength of the Royal Navy; this is equivalent to 38,500 long tons (39,100 t) of aircraft.
Scaling the design back to 19,250 long tons (19,560 t) allowed two ships to be built to the designated tonnage. During the design process for what would eventually become the Graf Zeppelin class, the size of the new aircraft was greatly increased. By the time the keel was laid for the first ship, named Flugzeugträger A (Flight Carrier A), in December 1936, it had reached 26,931 long tons (27,363 t). Work progress continued to increase as the plan was revised; by 1939 it had risen to 28,090 long tons (28,540 t).
By the time the first ship, now named Graf Zeppelin, was launched in 1940, it had reached 33,500 long tons (34,000 t) displacement.
Full Size Printed Plans Vintage 1962 Semi Scale 1:300 “graf Zeppelin”
No ship is finished. The navy decided that it would take a long time to complete the single ships, and since the anti-aircraft guns of the Graf Zeppelin could be used to strengthen the Norwegian defenses directly defeated, the navy's order was convinced Hitler to begin construction on both ships immediately. , and Flugzeugträger B broke up shortly after.
But by January 1943 Hitler - enraged by the naval defeat at the Battle of the Barts Sea, where two cruisers were isolated by an escort - ordered the ship to be scrapped again.
The ship was destroyed in 1945 as the Soviet Red Army advanced, but she was raised and confiscated by the Soviets after the war. Its final fate remained unclear for many years until Soviet records were released after the end of the Cold War. She was sunk by the Soviet Navy in July 1947 during weapons tests;

By early 1942, the German Navy had realized the importance of aircraft, especially after the British attack on the Italian fleet at Taranto in 1940 and the loss of the German battleships. of Bismarck in 1941. Therefore the Navy selected ships to work in auxiliary services. be converted. aircraft in May 1942, including passenger aircraft
Update 0.9.6: German Carriers
Future german aircraft carrier, aircraft carrier, german aircraft carrier graf zeppelin, german aircraft carrier ww2, german aircraft, aircraft carrier museum ships, modern german aircraft carrier, german aircraft carrier i, german carrier, german navy ww2 aircraft carrier, world war 2 german aircraft carrier, german navy aircraft carrier

0 Comments